NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 - Ecosystem
Related Chapters

















FAQs on NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 - Free PDF
1. What are the Important Topics Covered in the Ecosystem Class 12 NCERT PDFs?
All the topics in the chapter Ecosystem Class 12 NCERT PDFs are of equal importance. Here is a list of all the important topics in the chapter.
Structure and Functions of Ecosystems,
Patterns and Components of Ecosystems,
Productivity,
Decomposition,
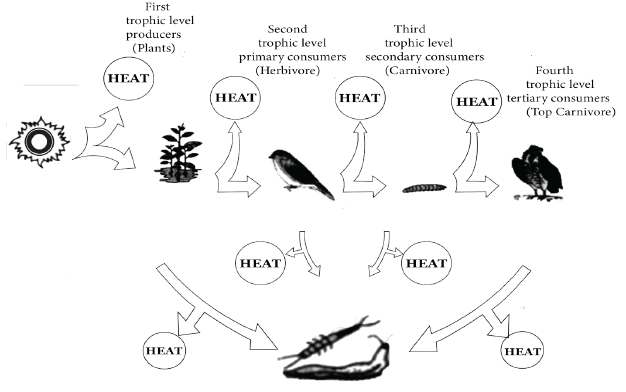
Energy Flow,
Ecological Pyramid,
Biomass,
Energy,
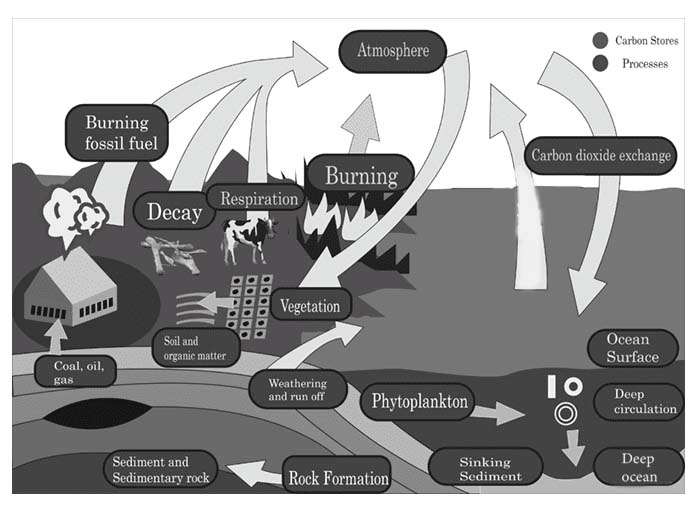
Nutrient Cycles (of Carbon and Phosphorous),
Ecological Succession
Ecological Services (carbon fixation, pollination, seed dispersal, and oxygen release).
These topics are explained in detail for the best understanding of the students in the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology's Chapter 14, available on Vedantu.
2. Are the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology's Chapter 14 Beneficial for Exam Preparation?
The NCERT solutions for class 12 Biology's Chapter 14 will help you to understand the chapter very well. In case you have some doubts for answering the questions given in the chapter and it becomes extremely difficult to understand the concepts properly, these NCERT Solutions will help you to address your doubts. All the topics covered in the 14th chapter of Class 12 NCERT Biology are thoroughly explained in the solutions.
3. Where can I get the accurate solution for NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 14?
Vedantu offers accurate and easy to understand NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology, Chapter 14. These solutions are crafted by the experts in Vedantu which provides authentic and knowledgeable information in a simplified manner. Visit the Vedantu website (vedantu.com) to download the free NCERT solutions PDF to learn and understand the concepts to ace your exams.
4. What are the topics covered in Chapter 14, Biology Class 12?
The topics covered are:
Ecosystem–Structure and Function
Productivity
Decomposition
Energy Flow
Ecological Pyramids
Ecological Succession
Nutrient Cycling
Ecosystem Services
To gain more knowledge on the mentioned topics, visit the Vedantu website and the app. It will provide you a deeper insight into this chapter. Students are advised to make use of the NCERT Solutions offered by the Vedantu to help them do well in their exams.
5. How important is Chapter 14 Of Class 12 Biology for board exams?
Ecosystem is one of the important topics and is given a lot of weightage in the board exams. Since the chapter is easily understandable, it will be easier for the students to answer the NCERT questions. Download the important questions PDF at the Vedantu Website or the app for free of cost.
6 . Which questions and answers are important in Chapter 12, Class 12 Biology?
Vedantu provides a series of important questions and answers. Visit the Vedantu website to download a PDF of important questions for Chapter 14, Class 12 Biology. These questions are crafted by the experts at Vedantu to make the revision easier for the students. With the NCERT Solutions provided by the Vedantu, students will get well versed in this chapter and excel in the exams.
7. What is Chapter 14 of Class 12 Biology all about
Students will learn about the structure and functions of an ecosystem. It will take you through the terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems too. You will also learn about Energy Flow, Ecosystem, and the Ecological Pyramid. Ecological Successions, Nitrogen Cycle and Phosphorus Cycle. To get in-depth knowledge, it is better for the students to get the help of NCERT Solutions. Visit the website to register for online live classes and download the PDF of NCERT solutions of Chapter 14 to revise and practice for the exams. Download the important questions at the Vedantu Website or the app for free of cost too.