NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 1 - Reproduction in Organism















FAQs on Class 12 NCERT Solutions for Biology Chapter 1
1. What will a Student get to Learn in the Chapter of Reproduction in Organism?
This chapter of CBSE 12 comprises the topics of asexual reproduction, reproduction necessity, budding, binary fusion, fragmentation, sexual reproduction, vegetation propagation, sexual reproduction in plants and advantages of sexual and asexual reproduction.
By studying this chapter, students will get to know the processes of reproduction in detail. Moreover, this unit focuses on female and male reproductive systems, plant reproduction, contraceptive methods and fertilisation. Reproduction is essential for the progression of species on the planet. If organisms stop reproducing, there will be a discontinuity of life.
2. How is DNA Important in Reproduction? Is it Related to Proteins?
DNA is exceptionally vital for all living creatures on earth, even in plants. They are essential for coding for proteins, inheritance and acts as a guide of genetic instruction for life and related processes. DNA stores the information for each cell’s or a living being’s development, reproduction and finally death.
DNA holds the codes for proteins, but the real protein is different from the codes available on DNA. The fundamental steps included are transcription, translation, and at last, modification and folding.
3. Why is an Offspring Born from Sexual Reproduction Likely to Survive More Than Asexual Reproduction?
The mode of sexual reproduction necessitates female and male gamete fusion. During the zygote formation process, exchange of traits and genes takes place between the gametes. Similarly, during the process of chromosome segregation and crossing over, chances of elimination of non-identical characteristics are much higher. Therefore, the offspring born does not resemble its parents and hence more chances of survival. However, if the mother parent is suffering from an acute disease like AIDS, etc., the child may not survive for long.
4. What is the advantage of Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions?
Our experts have framed the solutions from the examination point of view and they are very easy for you to learn. They have explained these solutions with supporting diagrams and examples in a simple language so that you can remember them for a longer time and our well-structured explanation will help you in scoring more marks.
We have drafted these solutions in a simple and understandable language. You can learn the solutions at any time and anywhere to improve your score in the examination. Our highly experienced teaching professionals are great in providing solutions and explanations for biology Class 12 reproduction in organisms chapter.
5. Define clones according to Chapter 1 of Class 12 Biology?
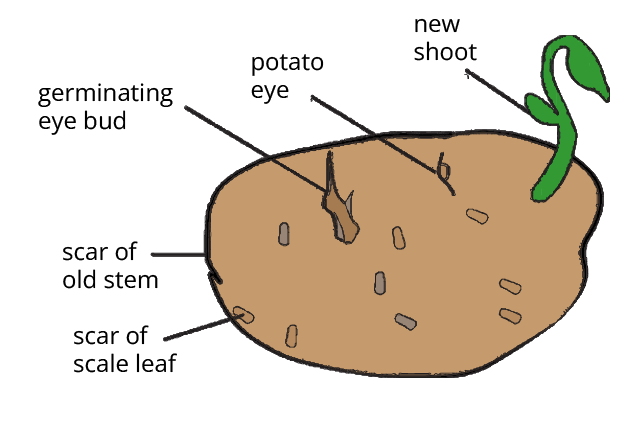
During an asexual reproduction there is only one parent involved and no fusion takes place between the male and the female gamete. The offspring produced by this kind of reproduction are identical genetically and also morphologically to the parent. The offspring that do not show any variations and are vulnerable to the environment are called clones. The chapter is well defined systematically in Vedantu which becomes easy for the students.
6. What are the chapters in Biology Class 12?
There are a total of 16 chapters in Biology Class 12.
They are
The Reproduction in Organisms.
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants.
Human Reproduction.
Reproductive Health.
Principles of Inheritance and Variations.
Molecular Basis of Inheritance.
Evolution.
Human Health and Diseases.
Strategies for Enhancement of Food Production.
Microbes in Human Welfare.
Biotechnology Principles and Processes.
Biotechnology and its Application.
Organism and Populations.
Ecosystem.
Biodiversity and conservation.
Environmental issues.
7. List out the important concepts discussed in NCERT Solutions for Chapter 1 of Class 12 Biology.
The important concepts discussed in NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology are Reproduction, Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants, Male And Female Reproductive Systems, Reproductive Health, Mendel’s Laws Of Inheritance, Genetics And Evolution, Common Diseases In Humans, Role Of Animal Husbandry, Microbes, Biotechnology, Biotechnological Applications In Agriculture, Hibernation, Nutrient Cycle, Biodiversity And Conservation, Air Pollution And Its Control, Water Pollution And Its Control.
8. What is Reproduction according to Chapter 1 of Class 12 Biology?
Reproduction is the process of living organisms giving birth to their young ones similar to them. This is a continuing process from one generation to another. If there is no reproduction, then the species will not live for a long time or may even become extinct. The world would have ended without this process.
9. Is Vedantu providing answers for NCERT Solutions for Chapter 1 of Class 12 Biology?
Yes, Vedantu provides the answer for NCERT Solutions for Chapter 1 of Class 12 Biology. You can download it using the link NCERT Solutions for Chapter 1 of Class 12 Biology and start preparing for the exams. The solutions provided are easy to understand. The answers are explained well, and one can rely on them for their preparation. The curriculum is updated, and there is no confusion. The sample papers and the important questions help the students in thorough preparation. These solutions are available free of cost on Vedantu (vedantu.com). You can download these using the Vedantu app as well.